Jing-Jen Lin, Jie-Yun Li and Ya-Hsuan Lin
Basic Concept
Product Concept
Freshwater clam (Corbicula fluminea) and the microalga Chlorella have been successfully cultured in Taiwan. The hot-water extract of freshwater clam and that of Chlorella have been commercialised as an essence with health claims for domestic consumption and export to Japan. The essence production resulted in a nutritious but underutilised material. The residual meat of clam consisted of 60% protein, while clam shell can be powdered as a natural calcium source. Chlorella residue contained 60% protein, 15% carbohydrate and 10% dietary fiber but all have been wasted.
The objective of this project is to use the abundant underutilised material, the residual clam meat from clam essence production, the Chlorella residue, a by-product from Chlorella essence production, and fortify the mix with powdered clam shell as a calcium-rich supplement to develop a product of ambient-temperature stability, ready-to-eat, high-protein, and high dietary fiber, low sodium, named “Quick Green Clambit Delight”. The processing operation of this product includes grinding, mixing, and packaging with biodegradable flexible material. The production requires low energy consumption. The water activity (aw) of the product was set at 0.6 that eliminates the risk of growth and toxin production by Clostridium botulinum. The final product is shelf-stable, and easy for storage and distribution. The whole concept of the product design is a green process from green microalgae, on which the freshwater clam feeds, indicative of the sustainability of a food chain that fights hunger and malnutrition.
Product Description
Product Name: Quick Green Clambit Delight.
Ingredients: Freshwater-clam meat, microalgae (Chlorella), clam-shell powder, salt, seasoning.
Characteristics: Ready-to-eat, high-protein, high-fiber, high-calcium, low-fat, low-sodium, low-sugar.
Packaging : Flexible biodegradable package (150 g/ packet).
Serving suggestions:
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Use as a nutritional supplement.
Target market: Protein-deficient population, high-fiber diet for senior citizens,
nutritional supplement for calcium deficient population.
Storage:
Shelf life: 12 months for unopened package.
Cost / Tentative selling price: US$ 1 / US$ 4.
Nutrition Labelling of Quick Green Clambit Delight
Proximate Composition
The proximate composition of Quick Green Clambit Delight and its raw material components are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Proximate composition of Quick Green Clambit Delight and its raw materials
|
Material |
Moisture |
Protein |
Fat |
NFE |
Fiber |
Ash |
|
Ca |
Na |
|
(%) |
|
(mg) |
|||||||
|
Clam meata |
1.5 |
60.2 |
10.8 |
26.3 |
- |
1.2 |
|
135 |
|
|
Chlorellaa |
7.9 |
58.7 |
11.2 |
3.5 |
11.2 |
7.5 |
|
94.0 |
|
|
Clam shellb |
|
1000 |
- |
||||||
|
Green Clambit |
3.9 |
58.1 |
10.7 |
17.1 |
4.2 |
3.5 |
|
1000 |
116 |
a Experimental data from our laboratory research
b According to Oikawa et al. (2000)
Health Claims
Freshwater Clam
Freshwater clam has hypocholesterolemic activity (Chen et al. 2008,Chijimatsu et al. 2008), has a hypotensive effect (Tsai et al. 2006), is hypolipidemic (Lin et al. 2011), and hepatoprotective activities (Chi et al. 2010). It also prolongates the lag phase of low density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation (Chen et al. 2008). The freshwater clam residual meat contains fat-soluble compounds, which demonstrate anti-inflammatory activity, including polyunsaturated fatty acids, pigments and phytosterols (Chijimatsu et al. 2011, Lin et al. 2012). The phytosterols have been shown to block the proliferation of HepG2, Hep3B and HL-60 (Huang et al. 2006, Kong et al. 2011).
Chlorella
Chlorella is a unicellular green microalga, which contains high levels of lutein and β-carotene (Ignacio and Jose 2008, Plaza et al. 2009), and is reported to show antioxidant activity (Amin 2008). Chlorella also exerts a hypoglycemic effect (Cherng and Shih 2005a, 2006), a lipid-lowering effect (Cherng and Shih 2005b, Shibata et al. 2007), and anti-inflammation activity (Guzmán et al. 2003).
Schematic Illustration of the Processing Steps of Quick Green Clambit Delight
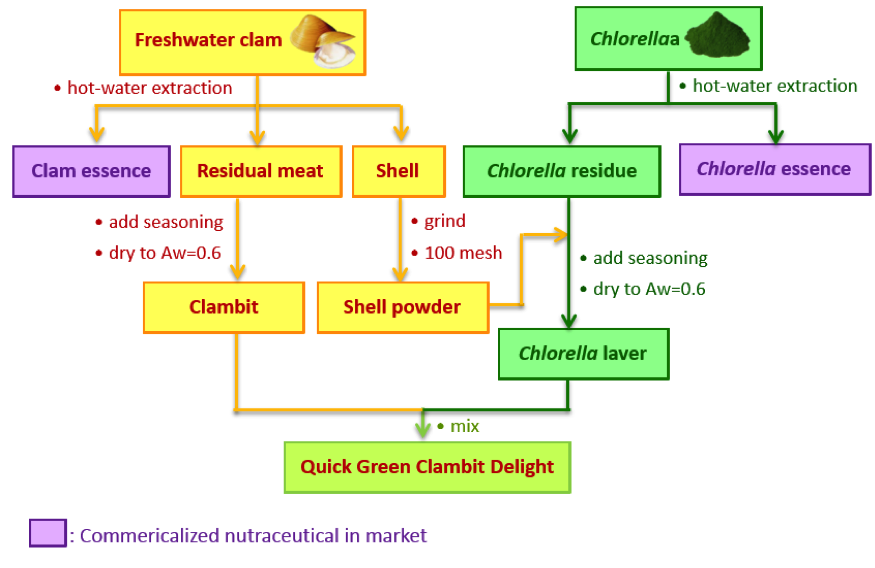
Process of Quick Green Clambit Delight
|
a. Clambit |
|
|
Ingredients |
|
|
|
|
|
Preparation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frozen dry to make the water activity (aw) < 0.6. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b. Shell powder |
|
|
Ingredients |
|
|
|
Freshwater clam shell |
|
Preparation |
|
|
|
Grinding the freshwater-clam shell. |
|
|
Filter the ground freshwater clam shells by the sieve (100 mesh). |
|
|
Dish up and reserve the fine shell powder. |
|
c. Chlorella dried film |
|
|
Ingredients |
|
|
|
|
|
Preparation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dry them in the 50℃ oven for 15-20 minutes to get the dried film. |
|
d. Quick Green Clambit Delight |
|
|
|
Dried clam and Chlorella mix: aw < 0.6 |
Table 2. Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) of Quick Green Clambit Delight
|
Process |
Potential hazards |
Significant harm |
Determine basis |
Precaution |
CCP Y/N |
||
|
Residual clam meat |
Biological |
Microbial food poisoning |
Yes |
GHP (Good Hygienic Practice) |
Water activity (aw) control |
N |
|
|
Physical |
Foreign body |
No |
Acceptance |
Pick out |
|
|
|
|
Chlorella residue |
Biological |
Microbial food poisoning |
Yes |
GHP |
aw control |
N |
|
|
Physical |
Foreign body |
No |
Acceptance |
Pick out |
|
|
|
|
Shell grind |
Biological |
Microbial food poisoning |
No |
GHP |
Regular disinfection |
|
|
|
Physical |
Foreign body |
Yes |
Acceptance |
Pick out |
N |
||
|
Clambit preparation |
Biological |
Microbial food poisoning |
Yes |
GHP |
aw control |
Y |
|
|
Chlorella layer preparation |
Biological |
Microbial food poisoning |
Yes |
GHP |
aw control |
Y |
|
|
Pack |
Biological |
Microbial food poisoning |
Yes |
GHP |
aw control Acceptance |
Y |
|
|
Physical |
Foreign body |
Yes |
Acceptance |
Pick out |
N |
||
|
Physical |
Printing oil pollution |
Yes |
GHP |
Acceptance |
N |
||
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank our advisor, Prof. Bonnie Sun Pan for her kind guidance, LiChuan Farm Ltd for providing freshwater clam residual meat, and Taiwan Chlorella Manufacturing Co. Ltd for providing Chlorella residue.
References
Amin, A (2008) Chemopreventive effect of Chlorella on the antioxidant system in 7, 12-dimethylben anthracene-induced oxidative stress in liver. Internat. J. Pharmacol. 4: 169-176.
Chen, TY, Lin, BC, Shiao, MS and Pan, BS (2008) Lipid-lowering and LDL-oxidation inhibitory effects of aqueous extract of freshwater clam (Corbicula fluminea) - using tilapia as an animal model. J.f Food Sci. 73: 148-153.
Cherng, JY and Shih, MF (2005a). Potential hypoglycemic effects of Chlorella in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Life Sci. 77: 980-990.
Cherng, JY and Shih, MF (2005b). Preventing dyslipidemia by Chlorella pyrenoidosa in rats and hamsters after chronic high fat diet treatment. Life Sci. 76: 3001-3013.
Cherng, JY and Shih, MF (2006) Improving glycogenesis in Streptozocin (STZ) diabetic mice after administration of green algae Chlorella. Life Sci. 78: 1181-1186.
Chi, HM, Chou, ST, Lin, SC, Su, ZY and Sheen, LY (2010) Protective effects of water extract of clam on normal and CCl4-induced damage in primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Am. J. Chinese Med. 38: 1193-1205.
Chijimatsu, T, Tatsuguchi, I, Abe, K, Oda, H and Mochizuki, S (2008) A freshwater clam (Corbicula fluminea) extract improves cholesterol metabolism in rats fed on a high-cholesterol diet. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 72: 2566-2571.
Chijimatsu, T, Umeki, M, Okuda, Y, Yamada, K, Oda, H and Mochizuki, S (2011) The fat and protein fractions of freshwater clam (Corbicula fluminea) extract reduce serum cholesterol and enhance bile acid biosynthesis and sterol excretion in hypercholesterolaemic rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. Brit. J. Nutr. 105: 526-534.
Guzmán, S, Gato, A, Lamela, M, Freire-Garabal, M and Calleja, JM (2003) Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of polysaccharide from Chlorella stigmatophora and Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Phytotherapy Res. 17: 665-670.
Huang, YT, Huang, YH, Hour, TC, Pan, BS, Liu, YC and Pan, MH (2006) Apoptosis-inducing active components from Corbicula fluminea through activation of caspase-2 and production of reactive oxygen species in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 44: 1261-1272.
Ignacio, RG and Jose, LG (2008) Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of three microalgal species for use as dietary supplements and in the preservation of foods. Food Chem. 108: 1023-1026.
Kong, Z., Yu, SC, Daia, SA, Tu, CC, Pan, MH and Liu, YC (2011). Polyoxygenated sterols from freshwater clam. Helv. Chim. Act. 94: 892-896.
Lin, CM, Lin, YL, Tsai, NM, Wu, HY, Ho, SY, Chen, CH, Liu, YK, Chiu, YH, Ho, LP, Lee, RP and Liao, KW (2012) Inhibitory Effects of chloroform extracts derived from Corbicula fluminea on the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. J. Agric.Food Chem. 60: 4076-4082.
Lin, YH, Tsai, JS, Hung, LB and Pan, S (2010). Hypocholesterolemic effect of compounded freshwater clam protein hydrolysate and Gracilaria. Food Chem. 123: 395-399.
Oikawa, K, Asada, T, Yamamoto, K, Wakabayashi, H, Sasaki, M, Sato, M and Matsuda, J (2000) Antibacterial activity of calcined shell calcium prepared from wild surf clam. J. Health Sci. 45: 98-103.
Plaza, M, Herrero, M, Cifuentes, A and Ibanez, E (2009) Innovative natural functional ingredients from microalgae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57: 7159-7170.
Shieh, IC., Fang, TJ and Wu, TK (2009) Isolation and characterization of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from the algae protein waste. Food Chem. 115: 279-284.
Tsai, JS, Lin JL, Chen, JL and Pan, BS (2006). The inhibitory effects of freshwater clam (Corbicula fluminea, Muller) muscle protein hydrolysates on angiotensin Ι converting enzyme. Process Biochem. 41: 2276-2281.
Jing-Jen Lin, Jie-Yun Li and Ya-Hsuan Lin are undergraduate students supervised by Professor Bonnie Sun Pan (e-mail: bonnie@ntou.edu.tw), National Taiwan Ocean University, No.2 Beining Road, Jhongjheng District, Keelung City 202, Taiwan (ROC).
This paper was awarded third place in the Undergraduate Product Development Competition held at the 17th IUFoST World Congress of Food Science and Technology, Montreal, Ontario, Canada on 17-21 August 2014.
IUFoST Scientific Information Bulletin (SIB)
FOOD FRAUD PREVENTION